Posted On : 15 July 2024
Introduction
The e-commerce world is highly competitive, with giants like Amazon and eBay dominating the market. However, smaller e-commerce businesses can still thrive by using advanced SEO strategies. These techniques can help you improve your online presence, attract more visitors, and increase sales. This article will cover key strategies to help your e-commerce business compete effectively.
1. Long-Tail Keywords Optimization
Definition and Benefits:
Long-tail keywords are specific phrases that customers are more likely to use when they are closer to making a purchase. These keywords are usually longer and more detailed.
Examples:
- A) Instead of "shoes," use "women's running shoes size 8."
- B) Instead of "laptops," use "affordable gaming laptops under $500."
Benefits:
- A) With less competition, easier to rank higher in search results.
- B) Higher conversion rates since they target customers ready to buy.
Researching Long-Tail Keywords
Tools and Methods:
| Free Tools | Paid Tools |
|---|---|
| Google Keyword Planner: Offers keyword suggestions and search volume. | Ahrefs Keyword Explorer: Offers a comprehensive set of data including search volume, keyword difficulty, click-through rate, keyword ranking history, parent topics, and related keywords. |
| Ubersuggest: Provides keyword ideas and competitive analysis. | SEMrush Keyword Magic Tool: Provides keyword suggestions, search volume estimates, keyword difficulty score, organic traffic potential, and related keywords. It also offers features like keyword trend analysis and competitor keyword research. |
| Moz Keyword Explorer (Free Limited Plan): The free plan offers a limited number of searches per month. | KWFinder: Offers keyword suggestions, search volume estimates, keyword difficulty score, and SERP (Search Engine Results Page) analysis to see which websites rank for those keywords. |
Analyzing Search Volume and Competition: Finding the Keyword Sweet Spot
Finding the right keywords is like finding the sweet spot on a Venn diagram. You want keywords with:
Decent Search Volume: Enough people search for the term to drive traffic to your site.
Low Competition: You have a reasonable chance of ranking well for the term.
Here are some techniques to analyze search volume and competition to find this sweet spot.
Understanding Search Volume:
Absolute vs. Relative Search Volume: Look beyond just the raw search volume number. Consider the relative search volume within your niche. A keyword with 1,000 searches per month might be fantastic for a small niche, but less impressive for a broader market.
Search Trends: Use tools like Google Trends to see how search volume fluctuates over time. Target keywords with stable or increasing search volume.
Long-Tail vs. Head Terms: Head terms (broad keywords) tend to have higher search volume but also much higher competition. Long-tail keywords (more specific phrases) have lower search volume but lower competition, making them easier to rank for and potentially converting better.
Analyzing Competition:
Keyword Difficulty Scores: Tools like Moz and SEMrush assign keyword difficulty scores based on factors like the number of competing websites and the strength of their backlinks. A lower score indicates less competition.
SERP Analysis: Manually review the top-ranking pages for your target keywords. Are they from large authority sites or smaller niche players? This can give you a sense of the competitive landscape.
Organic Traffic Estimates: Some tools estimate the amount of organic traffic a keyword can potentially drive. This can help you prioritize keywords with higher traffic potential.
Techniques to Find Keywords with the Right Balance:
Start Broad, Refine Narrow: Begin with broad seed keywords related to your niche. Use keyword research tools to generate long-tail variations and filter based on search volume and competition.
The “Goldilocks” Approach: Don’t just chase the highest search volume. Aim for keywords with a search volume that aligns with your traffic goals and a competition level you can realistically compete against.
Look for Niche Opportunities: Explore forums, social media groups, and industry publications to identify keywords used by your target audience that competitors might not heavily target.
Remember keyword research is an iterative process. As you gain insights and your website grows, you can refine your keyword strategy and target more competitive terms over time.
Implementing Long-Tail Keywords
- Product Descriptions: Include long-tail keywords naturally in your product descriptions.
- Meta Tags: Use these keywords in title tags and meta descriptions.
- Blog Content: Write blog posts targeting these keywords.
2. Content Marketing and Blogging

Importance of Content Marketing
Content marketing can drive organic traffic and improve search rankings. It helps establish your brand as an authority in your niche.
Creating High-Quality Content
Types of Content:
- A) Product Guides: Detailed guides on how to choose and use your products.
- B) How-To Articles: Step-by-step instructions related to your products.
Tips for Writing Engaging and SEO-Friendly Content:
- A) Use clear, simple language.
- B) Include relevant keywords naturally.
- C) Add images and videos for better engagement.
Example:
If you sell gardening tools, write a blog post titled “How to Choose the Right Gardening Tools for Beginners.”
Setting Up a Blog:
- Ensure your blog is part of your main website.
- Use a clean and easy-to-navigate design.
- Regular Posting Schedule and Topic Ideas:
- Post at least once a week.
- Plan topics in advance, such as seasonal trends, product updates, and customer stories.
3. Technical SEO Enhancements

Website speed is crucial for SEO and user experience. People are impatient, and slow loading times can lead to bounce rates and lost sales. Here’s how to optimize your website for speed:
Understanding the Problem:
- A) Load Time Components: Website load time is impacted by various factors like server response time, image size, and the number of external files.
- B) The Impact of Slow Speed: Studies show that even a slight delay can significantly increase bounce rates and decrease conversions.
Tools to Test Site Speed:
Google PageSpeed Insights
This free tool by Google analyzes your website's performance on desktop and mobile devices and offers specific recommendations for improvement.
GTmetrix
Another free tool that provides detailed performance reports, including page load time, waterfall charts, and actionable optimization suggestions.
Techniques to Reduce Load Times:
1. Compress Images: Images are often the biggest culprit behind slow loading times.
Techniques: Use tools like TinyPNG or Kraken.io to compress images without sacrificing significant quality.
Consider: Explore different image formats like JPEG or WebP, which can offer better compression for specific image types.
2. Minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML: Minification involves removing unnecessary characters like whitespace, comments, and formatting from code files.
Benefits: This reduces file size and improves loading speed.
Tools: Many free online tools and plugins can minify your code. minifier.org is one such tool.
3. Leverage a Content Delivery Network (CDN):
What is a CDN? A CDN is a network of geographically distributed servers that store cached copies of your website’s static content (images, JavaScript, CSS).
Benefits: When a user visits your site, their request is routed to the nearest CDN server, reducing latency and improving load times, especially for users in faraway locations.
Additional Techniques:
Reduce HTTP Requests: Fewer files mean fewer requests to the server, which improves speed. Combine multiple CSS and JavaScript files into single files when possible.
Optimize Server Response Time: Work with your web hosting provider to ensure your server has sufficient resources to handle traffic efficiently.
Enable Browser Caching: Caching allows browsers to store website elements locally, reducing the need to download them on every visit.
Optimize Database Queries: If your website uses a database, ensure queries are efficient and avoid unnecessary data retrieval.
Mobile Optimization
Importance of Mobile-Friendly Design:
Mobile Traffic Dominance: Over half of all web traffic now comes from mobile devices. If your website isn’t optimized for mobile, you’re missing out on a significant portion of your potential audience.
SEO and Mobile-First Indexing: Google prioritizes mobile-friendly websites in search results. A mobile-friendly design ensures your website ranks well on mobile searches.
Enhanced User Experience: Mobile users expect a seamless experience. A website that’s difficult to navigate or has elements that don’t display properly on a mobile device will frustrate users and lead to them bouncing off your site.
Responsive Design Principles:
Responsive design: It is the foundation of mobile optimization. It ensures your website automatically adjusts its layout and elements to fit the screen size of the device being used (desktop, tablet, mobile). Here are some key principles:
Flexible Layouts: Move away from fixed-width layouts. Use fluid grids and percentages to ensure your website elements resize and rearrange themselves for optimal viewing on any device.
Readable Text without Zooming: Fonts should be large enough to read comfortably on a mobile screen without the need for zooming in.
Optimize Images for Mobile Devices: Large images can slow down loading times. Use tools to compress images for mobile viewing while maintaining acceptable quality. Consider responsive image formats that adapt to different screen sizes.
Tappable Buttons and Clickable Elements: Ensure buttons and clickable elements are large enough for easy tapping on a mobile touchscreen.
Prioritize Content: Mobile users have smaller screens and shorter attention spans. Prioritize the most important content and functionality for the mobile experience.
Additional Mobile Optimization Techniques:
Fast Mobile Load Times: Implement the speed optimization techniques mentioned earlier, as they are even more critical for mobile users on slower data connections.
Avoid Flash and Pop-ups: Flash content is not supported on most mobile devices, and pop-ups can be intrusive on small screens. Opt for alternative solutions.
Test on Different Devices: Use browser developer tools or mobile emulators to test your website’s functionality and appearance across various mobile devices.
Importance of a Clean URL Structure:
Search Engines and URLs: Search engines use URLs to understand the hierarchy and content of your website. Clear and descriptive URLs help them categorize your pages effectively.
User-Friendly URLs: Human users also benefit from clear URLs. Short, descriptive URLs that reflect the content of the page are easier to understand and remember.
Best Practices for URL Structure:
Keep it Short: Aim for URLs that are concise and to the point, ideally under 60 characters.
Descriptive: Use keywords that accurately reflect the content of the page.
Readability: Use hyphens to separate words for better readability.
Avoid Complexity: Steer clear of excessive numbers, special characters, or dynamic parameters in your URLs.
Internal Linking Strategies:
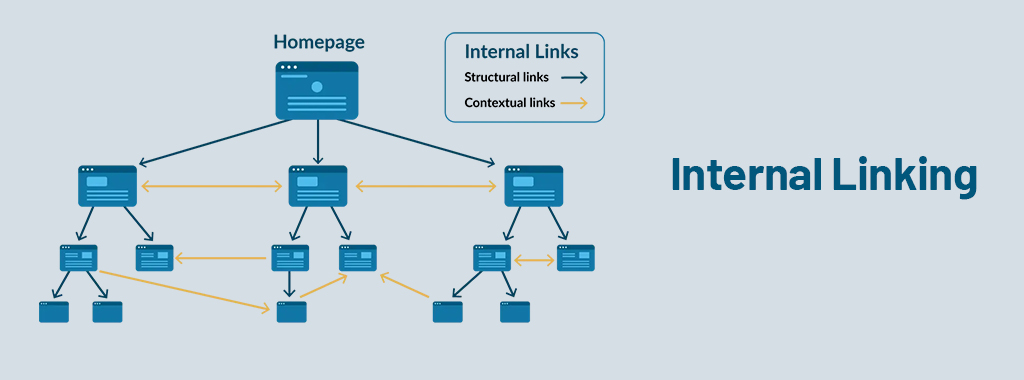
Internal linking refers to the practice of linking between different pages on your website. An effective internal linking strategy has several benefits:
Improved Navigation: Strategic linking helps users find related content and navigate your website more easily.
SEO Benefits: Internal links distribute SEO value throughout your website, helping search engines understand the relationships between your pages and improve your overall ranking.
Tips for Internal Linking:
Link Relevant Content: Link to pages that are topically relevant to the current page.
Anchor Text: Use descriptive anchor text that includes relevant keywords.
Link Depth: Aim to have all your important pages accessible within 3-4 clicks from the homepage.
4. Leveraging Schema Markup

Introduction to Schema Markup
Schema markup is code you add to your website to help search engines understand your content better.
Types of Schema Markup for E-commerce:
There are various schema markup types relevant to e-commerce websites. Here are two important ones:
Product Schema: This schema type provides detailed information about your products, such as:

Review Schema: This schema type allows you to display star ratings and customer reviews from your website directly in search results. This can significantly boost trust and click-through rates.
Benefits of Schema Markup:
There are several compelling reasons to implement schema markup for your e-commerce website:
Improved Search Visibility with Rich Snippets: Rich snippets are enhanced search results that display additional information about your products beyond just the title and URL. This can include product images, ratings, pricing, and availability. Rich snippets tend to stand out more in search results, potentially leading to higher click-through rates.
Increased Click-Through Rates: By showcasing key product information like star ratings and pricing directly in search results, schema markup can entice users to click through to your website and learn more.
Enhanced Brand Awareness: Rich snippets with your brand logo can increase brand recognition in search results.
Potential for Voice Search Optimization: Schema markup can help search engines understand your content better, which might improve your website’s visibility in voice search results.
Implementation:
Schema markup can be implemented using various methods, including JSON-LD, Microdata, and RDFa. JSON-LD is generally considered the easiest and most recommended format. Many website builders and content management systems (CMS) offer plugins or extensions to simplify schema markup implementation.
5. User-Generated Content
Importance of User-Generated Content
- Reviews, ratings, and testimonials can boost SEO by providing fresh content and building trust.
- Encouraging Customer Reviews
Strategies:
- Send follow-up emails requesting reviews.
- Offer incentives like discounts or free samples.
- Integrating User-Generated Content
- Displaying Reviews and Ratings:
- Add reviews and ratings to product pages.
- Highlight positive testimonials in blog posts and social media.
- Monitoring and Managing Reviews
- Responding to Reviews:
- Thank customers for positive feedback.
- Address negative feedback constructively and offer solutions.
6. Optimize for Local SEO (if applicable)
If your e-commerce store has a local presence, optimize your website and listings for local searches.
Examples:
- Include your city/region in titles and meta descriptions.
- Claim your Google My Business listing.
- Target local long-tail keywords like “best organic skincare products near me.”
7. Seasonal SEO
Identify Seasonal Trends:
- Use tools like Google Trends to spot seasonal spikes in demand.
- Plan content and promotions around these trends.
- Content Optimization
- Product Descriptions and Titles:
- Update descriptions and titles with seasonal keywords.
- Keep the content readable and natural.
- Seasonal Website Design:
- Use seasonal themes in your design.
- Update banner images, color schemes, and layouts to match the season.
- Blog Posts and Landing Pages
- Create content focused on seasonal trends and buying guides.
- Target long-tail keywords with high search intent.
8. Prioritize Voice Search Optimization

With the rise of voice search, optimize your product descriptions and content for natural language queries.
Understanding Voice Search Queries:
Conversational Language: Voice search queries tend to be phrased more like natural conversation than typed keywords. People ask questions and use longer phrases.
Focus on Intent: Voice search users often have a specific goal in mind. They might be looking for information, comparisons, or specific products.
Optimizing for Voice Search:
1. Target Long-Tail Keywords with Questions:
Shift from “buy shoes” to “where can I buy comfortable running shoes?” Instead of focusing solely on product-specific keywords, target long-tail keywords phrased as questions people might ask while searching by voice.
Think Location: If your business has a local presence, incorporate location-based keywords like “best [product type] near me”.
2. Leverage Natural Language Processing (NLP):
Understand Search Intent: While exact keyword matching is less important in voice search, understanding the user’s intent behind the query is crucial. NLP can help you analyze search queries and identify the underlying intent to optimize your content accordingly.
3. Incorporate FAQs into Your Content:
Anticipate User Questions: Create FAQ sections on your product pages and blog posts that address common questions users might ask about your products or the problems they solve.
Use Natural Language: Phrase your FAQs and content in a conversational tone, mimicking the way people speak in natural conversation.
4. Optimize for Featured Snippets:
Answer the Question Concisely: Voice assistants often read snippets from web pages in response to voice search queries. Aim to have your content answer the user’s question concisely and directly within the first paragraph or two, increasing your chances of being featured in a snippet.
Additional Techniques:
Mobile-First Optimization: Since most voice searches happen on mobile devices, ensure your website is mobile-friendly and offers a fast loading experience.
Structured Data and Schema Markup: While not a direct voice search ranking factor, schema markup can help search engines understand your content better, potentially improving your search visibility for relevant voice queries.
Examples:
Product Descriptions: Instead of just listing features, focus on how the product benefits the user.
Before: “Running shoes with maximum cushioning”
After: “Looking for comfortable running shoes that provide great shock absorption? Our cushioned running shoes offer maximum support for your long runs.”
Blog Posts: Create content that answers common user questions in a conversational style.
Topic: Best laptops for students
Title: “Struggling to find the right laptop for school? Here’s what you need to consider!”
9. Create a Data-Driven Internal Linking Strategy
Techniques for a Data-Driven Internal Linking Strategy:
1. Leverage Website Analytics:/p>
Tools: Utilize website analytics tools like Google Analytics to identify your high-performing pages. These pages are typically landing pages, blog posts, or product categories that receive significant organic traffic or user engagement.
2. Analyze User Behavior:
Go Beyond Traffic: Look beyond just page views. Consider metrics like time on page, bounce rate, and internal linking behavior within high-traffic pages. This can reveal user intent and how users are (or aren’t) navigating your website.
3. Identify High-Engagement Content:
Focus on User Engagement: Look for pages with high average time on page or low bounce rates. These pages are likely engaging users and keeping them interested.
4. Link to Relevant Lower-Traffic Pages:
The Bridge Builder: Use the insights from high-traffic and engaging pages to identify relevant lower-traffic pages that could benefit from being linked.
Optimize Anchor Text: When linking, use descriptive anchor text that incorporates relevant keywords related to the target page.
Benefits of a Data-Driven Approach:
Strategic Linking: By linking from authoritative pages to relevant lower-traffic pages, you distribute SEO value and can potentially improve the ranking of those pages.
Improved User Journey: Strategic linking guides users towards relevant content, keeping them engaged and exploring your website further. This can lead to increased conversions and sales.
Data-Backed Decisions: A data-driven approach removes guesswork from internal linking. You can prioritize linking opportunities based on actual user behavior and website performance data.
Examples:
High-Traffic Blog Post: A blog post on “Best Running Shoes for Beginners” has high traffic and engagement.
Lower-Traffic Product Pages: You can link from this blog post to specific product pages featuring running shoes suitable for beginners, using relevant anchor text like “lightweight running shoes” or “comfortable running shoes for new runners”.
By implementing these advanced SEO strategies, smaller e-commerce businesses can effectively compete with industry giants and improve their online presence.
Read more: Top 5 IT Software Outsource Development Companies in Singapore